Azure Blob Storage. Overview
Azure Blob Storage provides storage to build powerful cloud-native and mobile apps. It Optimizes costs with tiered storage for your long-term data, and flexibly scale up for high-performance computing and machine learning workloads.
The following is an overview about this Microsoft technology.
Overview on what is Azure Blob storage
Azure Blob storage is Microsoft's object storage solution for the cloud. Blob storage is optimized for storing massive amounts of unstructured data. Unstructured data is data that doesn't adhere to a particular data model or definition, such as text or binary data.
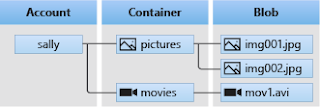 |
| Image taken from Official Azure Blob page. |
Accounts
A storage account provides a unique namespace in Azure for your data. Every object that you store in Azure Storage has an address that includes your unique account name. The combination of the account name and the Blob Storage endpoint forms the base address for the objects in your storage account.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/storage-blobs-introduction#storage- accounts
Types of Accounts
Azure Storage offers several types of storage accounts. Each type supports different features and has its own pricing model.
The following shows an overview of the different Azure Storage types of storage accounts:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/storage-account- overview?toc=%2Fazure%2Fstorage%2Fblobs%2Ftoc.json#types-of-storage-accounts
Move data to Blob storage
Azure Data Factory supports copying data to and from Blob storage by using the account key, a shared access signature, a service principal, or managed identities for Azure resources. For more information, see Copy data to or from Azure Blob storage by using Azure Data Factory.
Authorization
Authorizing requests against Azure Storage with Azure AD provides superior security and ease of use over Shared Key authorization. Microsoft recommends using Azure AD authorization with your blob applications when possible to assure access with minimum required privileges.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/authorize-data- access?toc=%2Fazure%2Fstorage%2Fblobs%2Ftoc.json#protect-your-access-keys
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/authorize-access-azure-active-directory
PHP Library
There is a way to interact with Azure Storage using PHP. Azure Storage PHP provides a set of client libraries that make it easy to access Microsoft Azure Storage services (blobs, tables, queues and files). For documentation on how to host PHP applications on Microsoft Azure
https://github.com/Azure/azure-storage-php
On the GitHub page there are all the requirements to setup a development environment to use it.
The following holds a quick example on how to use the library:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/storage-quickstart-blobs-php?tabs=linux
Conclusion
The architect of each development team should analyze all scenarios to decide the account type to select.
The account should be configured in order to allow the resources access. Roles management must be done, as well as container management, Roles Assignments, etc.
The authentication should be done through Azure AD service.
Comments
Post a Comment